The exchange of creatures between two Game Boy Advance systems running a specific iteration of the Pokmon series, facilitated via a link cable, allowed players to obtain Pokmon not natively available in their own game, complete their Pokdex, or battle with teams composed of Pokmon collected from multiple sources. For example, a player seeking a specific Pokmon only found in another version of the same generation could acquire it through this method.
This functionality was vital for achieving complete collection goals within the game, offering a collaborative element to what was primarily a single-player experience. It also added depth to the battling scene, enabling trainers to access a wider variety of strategic options. Its initial implementation in the broader franchise revolutionized the way players interacted with each other, fostering a community around shared goals and competitive spirit.
Subsequent sections will delve into the specifics of setting up the connection, understanding compatibility limitations, and exploring potential issues that may arise during the data transfer process.
Tips for Facilitating Data Exchange
Successfully executing the transfer of data requires careful attention to detail and an understanding of the system’s limitations. The following guidelines provide valuable insights to ensure a smooth and error-free experience.
Tip 1: Ensure Hardware Compatibility: Verify that both Game Boy Advance systems, or Nintendo DS systems operating in Game Boy Advance mode, and the link cable are functioning correctly. A faulty connection can interrupt the process and lead to data corruption.
Tip 2: Check Battery Levels: Insufficient battery power in either system can cause the process to fail. Ensure that both devices are adequately charged or connected to a power source before initiating the data transfer.
Tip 3: Navigate to the Pokmon Center: The designated location for accessing the feature is within the in-game Pokmon Center. Speak to the non-player character (NPC) located on the second floor to initiate the process.
Tip 4: Be Mindful of Game Compatibility: Only certain games are directly compatible. Transfers can occur between versions of the third generation, but cross-generational exchange requires additional steps and may not be possible for all Pokmon.
Tip 5: Avoid Disruptions: Refrain from interrupting the connection while data is actively being transferred. Powering off either system or disconnecting the link cable mid-process may result in corrupted data on one or both cartridges.
Tip 6: Confirm the Process Completion: After the exchange is complete, verify that the creatures have been successfully transferred to the intended game before saving. This ensures no data loss occurs.
Adhering to these guidelines minimizes the risk of errors and ensures the secure and efficient transfer of creatures. These practices contribute to a more enjoyable and less frustrating experience.
The subsequent section will address common troubleshooting steps for when these types of data interactions encounter problems.
1. Connectivity requirements
Successful data exchange is predicated on fulfilling specific connectivity requirements. This facet represents the foundational layer upon which the entire transfer process is built. Without the establishment of a stable and functional connection between two Game Boy Advance systems, the in-game mechanics designed to facilitate this action are rendered inert. For example, a faulty link cable, damaged port, or insufficient contact can prevent the two systems from recognizing each other, thus halting any attempts to exchange creatures. This foundational element is directly causal: deficient connectivity invariably leads to unsuccessful data transfer attempts.
The practical significance of understanding and meeting the connectivity requirements extends beyond simply initiating the transfer process. It directly impacts the integrity of the data being moved. An unstable connection can lead to data corruption during the process, resulting in loss of creatures or damage to save files. For example, if the link cable is accidentally disconnected mid-transfer due to poor connection, the progress might halt, and potential error with the game’s database might occur. The potential for these adverse effects underscores the importance of ensuring that all physical components are in optimal working condition prior to initiating the function.
In summation, stable connection is not merely a preliminary step, but a critical component integral to a successful and secure function. Challenges in establishing and maintaining a reliable connection pose a significant impediment to achieving the desired outcome of a proper exchange of creatures. A meticulous approach to evaluating and addressing potential connectivity issues is necessary to mitigate the risks and guarantee a positive experience.
2. Pokmon Center Access
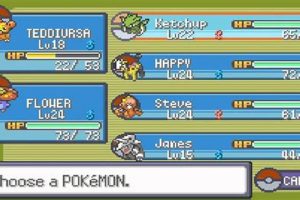
The Pokmon Center serves as the designated in-game location for initiating creature exchanges in the specified iteration of the franchise. It represents a critical access point, enabling players to interact with the data transfer mechanics integral to completing their Pokdex or battling using creatures from multiple game cartridges.
- Designated NPC Interaction
Within the Pokmon Center, a specific non-player character (NPC) facilitates the process. This NPC, typically located on the second floor of the Center, acts as the conduit between the player and the data transfer system. Initiating a conversation with this character prompts the necessary menus and options to appear, allowing players to prepare for and execute the exchange. Without interacting with this NPC, access to the data transfer functionality remains unavailable.
- In-Game Protocol Enforcement
Requiring players to access the data transfer functionality via the Pokmon Center enforces a specific protocol within the game’s environment. This design choice likely serves to maintain a level of order and control over the data transfer process, preventing unintended interactions or glitches that might arise from allowing such functionality in other game locations. This protocol dictates where and how the process can take place.
- Safety Mechanism for Data Integrity
The Pokmon Center, as a location of safety and healing within the game, provides a fitting environment for a process as sensitive as data transfer. The design reinforces the expectation that data is handled with care within the bounds of the function. Its implementation as a necessity represents a fundamental approach to ensuring a degree of inherent stability and minimizing the potential for data loss or corruption.
The deliberate connection between the Pokmon Center and the creature transfer mechanics reinforces the controlled and secure nature of the exchange process. This in-game access point reflects a deliberate design choice intended to safeguard the integrity of the data and manage player interaction within the established game framework.
3. Game Compatibility
Compatibility serves as a foundational constraint dictating the parameters within which creatures can be exchanged. Understanding which versions of the game can interact is crucial to avoid errors or failed transfer attempts. The ability to engage in these exchanges is predicated on adherence to pre-defined compatibility standards implemented by the game developers.
- Generation-Specific Constraints
The primary constraint is that data exchanges are predominantly limited to games within the same generation. Specifically, this iteration of the franchise can reliably exchange creatures with other third-generation games, such as Ruby, Sapphire, FireRed, and LeafGreen. Attempting to directly transfer data between generations (e.g., from a second-generation game like Pokmon Crystal) is not possible without employing additional hardware or software. This generation specific limitation is intrinsic to the game design.
- Version Exclusivity and Collaboration
Even within compatible generations, certain Pokmon are exclusively available in particular versions. This intentional design encourages players to collaborate and execute data exchanges in order to acquire creatures not found in their own game. For example, a player possessing Ruby and another possessing this installment of the franchise might exchange version-exclusive creatures to complete their Pokdex. This system promotes interconnectedness and fosters social interaction.
- Link Cable Requirements
While the games themselves must be compatible, the physical connection also adheres to specific constraints. Original Game Boy Advance systems and Nintendo DS systems operating in Game Boy Advance mode require a Game Boy Advance link cable for data exchange. Wireless adapters, introduced later in the franchise, are not typically supported for this particular game’s data transfer functionality. This hardware dependency necessitates the use of the correct physical cable.
- Regional Variations
In some instances, regional variations of the game may present compatibility challenges. Games released in different regions (e.g., North America, Europe, Japan) might have slight variations in their code or functionality, which could lead to unforeseen issues during data exchange. It’s essential to verify compatibility based on the specific regional release of each game involved in the data transfer process. Regional variations may impose unexpected barriers to the desired exchanges.
These factors demonstrate that the exchange of creatures within this specific title is not a universal feature applicable across all iterations of the franchise. Adherence to generation constraints, leveraging version exclusivity, utilizing the correct physical cables, and accounting for regional variations are essential for achieving successful collaboration. These elements work in concert to define the parameters of compatibility, shaping the ecosystem of the creatures and their journey across different game versions.
4. Process completion verification
Verification of process completion represents a critical failsafe mechanism integral to the function. After the data transfer between two Game Boy Advance systems, a confirmation step is essential to ensure the creatures have been successfully moved and the exchange is finalized. This phase mitigates the risk of data loss or corruption that can arise from interruptions or errors during the transfer. This step confirms the success, safeguarding against data inconsistencies.
The practical significance of this verification step is exemplified by scenarios where a system’s battery may fail during the transfer, or the link cable may become disconnected. Without verification, the player may unknowingly assume that the process was successful, only to later discover that the creatures have not been properly transferred and are potentially lost. The confirmation phase provides an opportunity to identify such errors and retry the process, safeguarding data integrity. For instance, the player should check both game files, after the trading sequence ends, to ensure that they have received the required Pokemons to avoid loss.
In summary, verifying completion of the creature exchange serves as a crucial component. It addresses inherent risks associated with data transfer, ensuring that the intended outcome is achieved and preventing potential data loss. It directly contributes to a more stable and reliable user experience.
5. Hardware stability
The stability of the hardware components involved is paramount for the successful exchange of data during the trading procedure. Disruptions due to unstable hardware can lead to corrupted data, incomplete transfers, or even damage to game cartridges. Maintaining stable functionality in both Game Boy Advance systems, as well as a secure connection through the link cable, directly impacts the integrity of the entire process. An example of such disruption occurs when one of the systems unexpectedly loses power mid-transfer, potentially corrupting save data. A malfunctioning link cable can also cause the process to fail to initiate or disconnect during the trade, resulting in an incomplete exchange of creatures. Addressing this factor head-on is essential to mitigate risks involved in data transfer.
Furthermore, understanding the practical implications of hardware stability extends to preventative maintenance. Regularly checking battery levels, ensuring the link cable is securely connected, and verifying that the Game Boy Advance systems are functioning correctly are crucial steps. Proper storage of the cartridges and cables, protecting them from physical damage or extreme temperatures, contributes to their long-term reliability. Ignoring these preventative measures increases the likelihood of encountering hardware failures during the data transfer process, potentially leading to frustration and data loss.
In summation, hardware stability represents a foundational element for the successful exchange. The integrity of this process is directly dependent on the reliable performance of the involved components. By recognizing the potential for hardware-related issues and proactively implementing preventative measures, the likelihood of encountering errors during data transfer can be minimized.
Frequently Asked Questions Regarding Trading Pokemon Emerald
The following section addresses common inquiries and clarifies misconceptions regarding data transfer within this specific title. These questions and answers aim to provide a comprehensive understanding of the process.
Question 1: What specific hardware is required for facilitating data exchange within Pokmon Emerald?
Data transfer necessitates two Game Boy Advance systems or Nintendo DS systems operating in Game Boy Advance mode, and a functional Game Boy Advance link cable. Wireless adapters are not supported for data exchange within the original implementation of this feature.
Question 2: Is it possible to exchange Pokmon between this version and games from other generations?
Direct exchange with games from previous generations (e.g., Pokmon Gold, Silver, Crystal) is not possible using the standard data transfer functionality. Transfer to later generations requires utilizing specific Nintendo DS titles with migration features.
Question 3: Where is the data transfer functionality accessed within the game itself?
The exchange process is initiated within the Pokmon Center. A non-player character (NPC), typically located on the second floor, provides access to the required menus and options.
Question 4: What factors can cause a data transfer to fail?
Several factors can disrupt data transfer, including a faulty link cable, insufficient battery power in either system, interruption of the connection during the process, incompatible game versions, or hardware malfunction.
Question 5: Can all Pokmon be exchanged between compatible game versions?
While most Pokmon can be exchanged, certain creatures may be subject to restrictions. Some legendary Pokmon, for instance, may require specific in-game conditions to be met before they can be transferred.
Question 6: What steps should be taken if a data transfer fails mid-process?
In the event of a failed transfer, it is crucial to avoid saving the game on either system. Attempt to re-establish the connection and repeat the process. In cases of data corruption, professional data recovery services may be required.
These questions and answers provide a concise overview of common concerns related to this game’s trading process. By addressing these aspects, a more informed and successful data transfer experience can be achieved.
Subsequent sections will delve into troubleshooting tips for resolving issues commonly encountered when transferring data.
Conclusion
The preceding exploration of trading Pokemon Emerald underscores its multifaceted nature within the broader context of the franchise. It is evident that successful data exchange is contingent upon a confluence of factors, ranging from hardware functionality and game compatibility to adherence to specific in-game protocols and diligent process verification. A comprehensive understanding of these elements mitigates the risk of data loss and promotes a more efficient experience.
Given the inherent complexities and potential challenges associated with trading Pokemon Emerald, the insights provided serve as a critical resource for players seeking to maximize their collection and fully engage with the game’s collaborative elements. Further research and community collaboration can only enhance the understanding of these intricate data exchange mechanisms and ensure the preservation of valuable digital assets.